NEWS
Neural network taught to see the mirrors in the frame
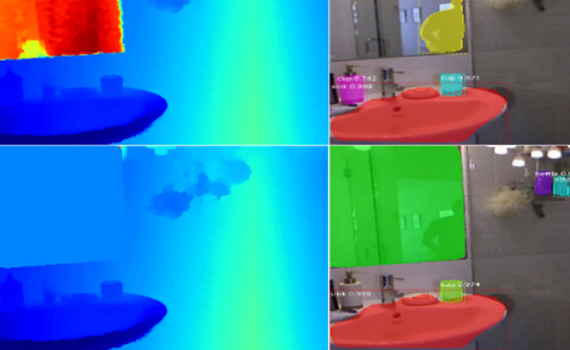
Chinese developers have taught the neural network to recognize mirrors in images. The algorithm does this because the areas of the image with and without a mirror usually differ in texture, color, and also semantic features.
Experiments have shown that a neural network produces mirrors in photographs better than other algorithms for this task, say the authors of an article that will be presented at the ICCV 2019 conference.
Mirrors are a big enough problem for computer vision algorithms. For example, when using algorithms for determining the depth in the image, the mirror is most likely to distort the data and cause the algorithm to “see” the reflected objects at a greater distance than the mirror itself is located. As a solution to this problem, the developers propose using mirror recognition algorithms, thanks to which the main algorithm could ignore this area in the picture. Such algorithms already exist, but so far they have low accuracy.
Developers from the City University of Hong Kong taught the algorithm to recognize mirrors in images and to select them qualitatively, so that then they can use computer vision algorithms on such processed images. The algorithm consists of two main parts.